
To connect a fiber optic cable to an SFP, put the right fiber connector into the SFP port. Make sure the connector fits and is clean. You need to use the correct fiber and SFP module. This helps you avoid problems. Handle everything with care. Dirt can cause most network problems.
80% of network owners say dirt causes problems.
98% of fiber cable installers say dirt is the main problem.
Single-mode fiber works for long distances. It can reach up to 100 kilometers. Multimode fiber is good for short distances. It usually works for less than 500 meters. Fiber uses light signals. Even a little dust can block the light and hurt how it works.
Always clean fiber connectors before you connect them. Dirt can stop light and cause problems in the network.
Pick the right fiber optic cable for your SFP module. Single-mode is good for long distances. Multi-mode works for short links.
Check connectors for damage before you use them. Look for scratches or dirt that can make signals weak.
Make sure your fiber connections are tight. Do not bend cables sharply. Keep cables neat to stop damage.
Test your connection after you set it up. Look at LED lights and use network tools to check if it works.
A fiber optic cable sends data using light pulses. It moves information faster than copper cables. The cable has a core that carries the light. Around the core, there is cladding, coating, a strength member, and an outer jacket. Each part protects the fiber and helps data move well.
Here is a table that lists the main parts and what they do:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Core | The middle part where light goes through. |
| Cladding | Keeps light inside the core and stops signal loss. |
| Coating | Stops the fiber from getting damaged. |
| Strength Member | Gives extra protection and keeps signals safe. |
| Outer Jacket | Guards the fiber from things outside. |
There are different kinds of fiber optic cables you can buy. For example, WCTX Tech sells single-mode and multi-mode cables. Single-mode fiber is good for long distances. Multi-mode fiber works for shorter distances. Fiber optic technology keeps getting better. New cables can go faster and last longer.
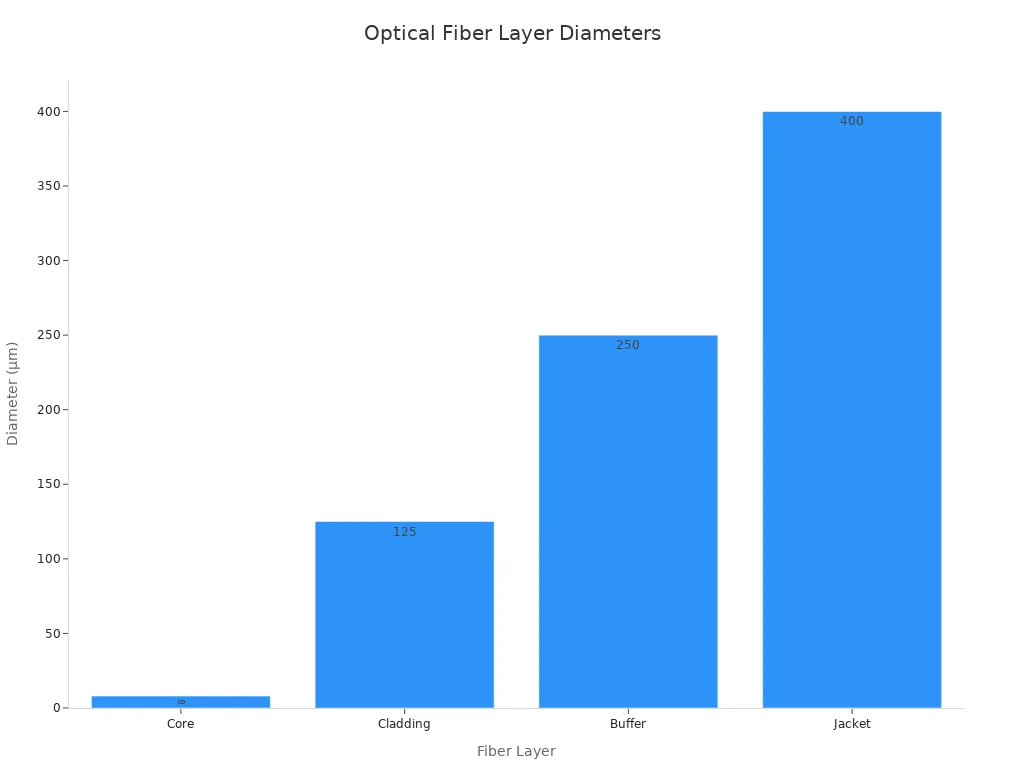
The way an optical fiber is built affects how it sends data. There are several layers, and each has its own size:
| Layer | Diameter (μm) |
|---|---|
| Core | 8 |
| Cladding | 125 |
| Buffer | 250 |
| Jacket | 400 |
A clean and organized fiber network has less noise. If you keep the layers safe and clean, you get better signals and fewer problems.
Fiber optic cables use light to send data far. The core and cladding have different refractive indices. This makes light bounce inside the core. The signal stays strong and does not escape. You get fast data with little loss.
Fiber optic cables move data faster and farther than copper cables. For example, fiber optic cables can reach speeds up to 400 Gbps. They can go over 12 miles at 10 Gbps. Copper cables usually stop at 1 Gbps and 300 feet.
Tip: Clean connectors and pick the right fiber type. This helps your fiber optic cable work its best.
You have to use the right fiber optic cable with the correct SFP module. There are a few things you need to check:
Wavelength matching: Both SFP modules should use the same wavelength. This helps your data move without mistakes.
Fiber type: Your cable needs to match the SFP transceiver. If you use single-mode fiber, both ends must support it.
Port compatibility: Some SFP ports only work with certain brands. Always look at your device’s details.
If you use the wrong fiber or SFP module, you might have trouble connecting. These problems can slow down your network or cause errors. Sometimes, your network may even stop working. You should always check the standards. For example, IEEE 802.3 and MSA help make sure your devices work together.
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| IEEE 802.3 | Supports different SFP speeds and distances |
| MSA | Makes sure SFP modules from different brands work together |
| SFF-8472 | Lets you watch SFP performance in real time |
| RoHS | Limits harmful materials in SFP modules |
Tip: Clean connectors before you connect them. Dust can block light and make signals weak.
There are different fiber optic cable connectors for SFP modules. The most common ones are SC and LC connectors. Each connector has special features:
| Feature | SC Connector | LC Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 2.5 mm diameter | 1.25 mm diameter |
| Mechanism | Push-pull | Latch-lock |
| Usage | Long-distance, enterprise | High-density environments |
| Advantages | Strong, easy to use | Small, fits many ports |
| Disadvantages | Bigger, needs more space | More fragile, compatibility |
SC connectors are good for big networks and long links. LC connectors are better for tight spaces, like data centers. Pick the connector that fits your SFP port and your network.
You need to choose between single-mode and multi-mode fiber optic cables. Each type works best for different jobs. Here is a comparison:
| Feature | Single-Mode Fiber | Multi-Mode Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Core Size | Smaller (8-10 microns) | Larger (50-62.5 microns) |
| Light Transmission Modes | One mode of light | Many modes of light |
| Attenuation | Lower over long distances | Higher over long distances |
| Bandwidth | Higher over longer distances | Lower over shorter distances |
| Typical Applications | Long-haul communications | Shorter, cheaper uses |
Single-mode fiber has a thin core. It lets light travel in one way. This means less signal loss and faster speeds over long distances. Multi-mode fiber has a wider core. It lets light travel in many ways, which causes more signal loss. Multi-mode fiber is best for short links, like inside buildings.
Pick single-mode fiber for long distances and fast speeds. Multi-mode fiber is good for short distances and saving money. WCTX Tech sells both types, so you can choose what works for your network.
Note: Always check how fiber optic cables work in your setup. Picking the right cable helps your signal and speed.
You have to clean fiber connectors before connecting them. Dust, oil, and fingerprints can block light. This can cause problems with your network. Even a tiny bit of dirt on the core can make signal loss worse. Your data may not work right. Always use a lint-free wipe or a special cleaning tool. Do not touch the end of the connector with your fingers.
Here are some common things that can make your network worse:
| Contaminant | Effect on Signal Transmission |
|---|---|
| Fingerprints | Can block light and make signal loss higher |
| Dust | Can block light and make signals weaker |
Cleaning fiber optic bulkhead adapters and ports is very important. Dust, oil, and other things can cause errors or even make your network stop working. You should check, clean, and check again both ends of a connector pair before you connect them.
Always look at, clean, and check both ends of a connector pair before you connect them. Looking closely helps you find scratches, pits, and dirt that can hurt the connector.
If your network gets slower or loses signal, clean the connectors right away. Watch the signal after you connect the cables. If you see problems, clean the cables again.
You need to check every fiber connector before using it. The IEC 61300-3-35 standard tells you how to check connectors. This standard splits the end face into four parts: core, cladding, adhesive, and contact. The core part has the strictest rules because it carries the light.
Follow these steps to check connectors:
Use a microscope to look at the end of the fiber.
Look for scratches, pits, or dirt in the core part.
If you see problems, clean the connector and check again.
Only use connectors that pass the check.
You should check all connectors, even new ones or ones from the factory. Clean connectors that do not pass the IEC 61300-3-35 check. Do not clean connectors that already pass, because cleaning can bring in dust.
A clean and safe fiber connector helps light move easily through the cable. This keeps your signal strong and your data safe. Checking and cleaning often protects your cables and keeps your network working well.
You need to follow a careful process to connect a fiber optic cable to an SFP module. This helps you keep your network fast and reliable. When you handle fiber, you protect the quality of light signals and prevent problems with data transmission.
Here is a step-by-step guide to help you insert the connector the right way:
Gather Your Equipment
Make sure you have the correct fiber optic cable and the right SFP module. Check that both match your network needs for speed and bandwidth. Wear anti-static gloves and wrist straps to protect the equipment from static electricity.
Inspect and Clean the Fiber
Look at the fiber connectors for any dirt or damage. Use a fiber optic cleaner to remove dust or fingerprints. Clean connectors help light move through the fiber without loss.
Insert the SFP Module
Hold the SFP module with the label facing up. Gently push it into the port on your network device until you hear a click. The click means the module is secure.
Remove Dust Caps
Take off the dust cap from the SFP module only when you are ready to connect. This keeps the optical interface clean and safe from dirt.
Connect the Fiber Optic Cable
Align the fiber connector with the SFP port. Push the connector in gently until you feel or hear a slight click. This click tells you the connector is in place and ready for signal transmission.
Connect the Other End
Plug the other end of the fiber optic cable into the device with another SFP transceiver. Make sure both ends are clean and secure.
Tip: Never look directly into the end of a fiber or SFP port. The light can harm your eyes.
Many people make mistakes during this process. Here are some common problems and how you can avoid them:
Dirty or damaged connectors can block light and weaken signals.
Poorly aligned connectors may cause signal loss or even stop data flow.
Bending or kinking the fiber optic cable can break the internal fibers and stop information from moving.
Using a cable that is too long for your SFP module can reduce speed and cause errors.
Too many connectors or splices in the path can lower signal quality.
You can avoid these mistakes by always inspecting and cleaning connectors, checking the fiber for bends, and making sure you use the right cable for the distance and speed you need.
After you insert the connector, you need to secure the connection. This step keeps your fiber optic cable safe and helps your network run smoothly. A secure connection protects the light signals and keeps your data moving at high speed.
Follow these best practices to secure your fiber connection:
Respect the minimum bend radius of the fiber. Do not bend the cable too tightly. Sharp bends can damage the fiber and block light signals.
Use cable management guides to keep cables organized. This prevents accidental pulls or bends that can hurt signal transmission.
Do not exceed the cable’s tensile strength. Pulling too hard can break the fibers inside.
Keep cables away from sharp edges. Use protective edging on cutouts to stop the cable from getting cut or pinched.
Avoid coiling the cable too tightly. Loose coils help protect the fiber and keep information flowing.
Regularly inspect and clean the connectors. Dust or dirt can build up over time and cause signal loss.
Do not remove protective plugs until you are ready to connect. This keeps the ends clean and safe.
Note: Good cable management not only protects your fiber but also makes it easier to find and fix problems if they happen.
When you secure the connection, you help keep the light moving through the fiber with little loss. This means your network can send data quickly and with fewer errors. You also protect the cable from damage, which helps your network last longer.
If you follow these steps, you will get the best performance from your fiber optic cables. You will see strong signals, fast speed, and reliable data transmission. Clean, secure connections help your network handle more bandwidth and keep information safe.
You must put in the SFP module the right way. This helps your fiber optic network work well. First, wear an ESD wrist strap. This stops static electricity from hurting your equipment. Do not take off the dust cover until you are ready to use the port. Find the TX and RX labels on the SFP module. These show you where to send and get signals.
Here are the steps to put in the SFP module:
Wear an ESD wrist strap to stop static damage.
Keep the dust cover on until you are ready to use the port.
Look for the TX and RX labels to help you.
Gently slide the SFP module into the port. Do not push hard.
Clean the fiber end before you take off the dust cover and connect the cable.
Make sure the module is in all the way.
Check for a green LED light. This means the connection works.
A secure SFP module helps your network run fast. It also keeps your equipment safe and your signals strong.
After you put in the SFP module and connect the fiber, check if it works. You can use different tools and signs to see if the link is good.
Look at the LED lights on the SFP module. If the light is on or blinking, the connection is good.
Check the optical power levels. Compare them to what the maker says is right.
Use network tools to test if data moves between devices.
Look at the logs on your network equipment. Watch for error messages or warnings about the module.
These steps help you know your fiber optic network is ready. You can trust your network to send information fast.
Sometimes, your fiber connection may have problems. Here are some common issues and how to fix them:
If the link goes on and off, check if the transceiver is in right and clean the optical part. Change the transceiver if it still does not work.
Do not use SFP and SFP+ modules together. They do not work with each other and can cause problems.
Use a visual fault locator to find breaks in the fiber. Change any cables that are broken.
Make sure you use the right fiber type with the transceiver. Use single-mode or multi-mode as needed.
If there is light but no connection, clean the end of the module and check if the cable is too long.
If the optical power is too high, use an optical attenuator to stop the receiver from getting too much light.
Keep your equipment in the right place. SFP modules work best in certain temperatures. Commercial ones work from 0°C to 70°C. Industrial ones work from -40°C to 85°C. Good cooling and cleaning help your fiber network stay strong.
Tip: Check and clean your fiber and equipment often. This keeps your network fast and protects your data.
You can connect fiber to SFP modules by following these steps:
Check that your fiber and SFP match in type and speed.
Clean and inspect all connectors before use.
Insert the SFP module and connect the fiber to the correct ports.
Power up your equipment and test the link.
Keep your fiber clean and handle it with care. Regular cleaning and careful installation help your networks run at top speed for many years. If you see errors, check the connectors and cables first.
You can use LC or SC connectors with SFP modules. Most modern SFPs use LC connectors because they fit in small spaces. Always check your device specs before you buy a Fiber Optic Cable.
Use a lint-free wipe or a special fiber cleaning tool. Never touch the connector end with your fingers. Clean connectors help your Fiber Optic Cable send strong signals.
No, you should not mix them. Single-mode SFPs need single-mode Fiber Optic Cable. Multi-mode SFPs need multi-mode cable. Mixing types can cause signal loss or connection failure.
Bending a Fiber Optic Cable too tightly can break the glass inside. This stops light from moving through the cable. Always follow the bend radius listed by the manufacturer.
Check the LED lights on your network device. A green light means your Fiber Optic Cable connection works. You can also test data speed with network tools or check for error messages.