
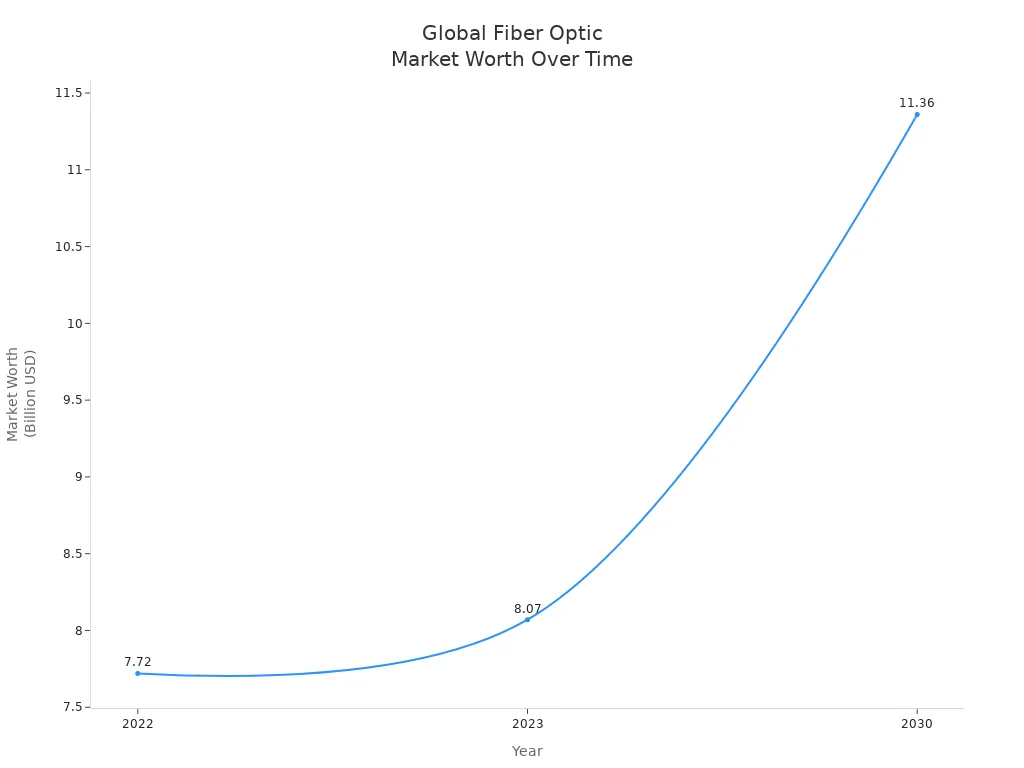
You see fiber optic cables in many new networks. They send data fast and do not fail often. There are two main types: single mode and multimode. Single-mode fiber is good for long distances and fast speeds. Multimode fiber is better for short distances and costs less. What you pick changes how fast and steady your network is. It also changes how much you pay. The fiber optic cable market is getting bigger. It may grow from $8.07 billion in 2023 to $11.36 billion by 2030.
Single mode fiber optic cables work well for long distances and fast speeds. They have a thin core and use lasers to send data with little signal loss.
Multimode fiber optic cables are good for short distances and cost less. They have a bigger core and use LEDs, so they are easier to put in.
When picking a fiber optic cable, think about how far your data must go. Single mode is best for long runs. Multimode is good for short connections.
Cost matters too. Single mode cables can cost more at first but last longer. Multimode cables are cheaper and easier to set up for short distances.
Think about what your network might need later. If you want to grow or need faster speeds, single mode fiber is a good pick.
A fiber optic cable is a special type of cable that carries information using light. You find these cables in many modern networks because they move data very quickly and with little loss. Each fiber optic cable contains thin strands of glass, called optical fibers. These strands are much thinner than a human hair.
The structure of a fiber optic cable includes two main parts:
The core, made from very pure glass, lets light travel through it with almost no loss.
The cladding, which surrounds the core, has a lower refractive index. This difference keeps the light inside the core by reflecting it back, even as it bends.
Note: The cladding acts as a barrier that stops light from escaping, so your data stays safe and strong as it moves through the cable.
Fiber optic cables use the science of total internal reflection. When you send light into the core at a certain angle, the cladding reflects the light back into the core. This keeps the light moving down the cable, even around corners.
Here’s how data transmission happens in a fiber optic cable:
Devices turn information into light pulses.
These light pulses travel through the optical fiber core.
The cladding keeps the light contained, so the signal does not weaken much, even over long distances.
At the other end, devices turn the light pulses back into information you can use.
This process allows fiber optic cables to send data much faster and farther than traditional copper cables. You get high-speed communication with very little signal loss, which is why fiber optic cables are popular for internet, phone, and TV networks.
There are two main types of optical fiber. These are single mode and multimode. Each type has its own structure. Each works best in different situations. Knowing the differences helps you pick the right cable.
Single mode fiber optic cable has a very thin core. The core is about 8 to 10 micrometers wide. This small core lets light travel in only one path. You get less signal loss. There is not much modal dispersion. Your data moves faster and farther without mixing up.
Tip: Single mode fiber is best for long distances and fast data.
Single mode fiber is used to send data far away. These cables use lasers or laser diodes for light. The light goes almost straight through the core. This keeps the signal strong. You find single mode fiber in global networks, data centers, and military systems.
Here is a quick look at how it works:
| Core Diameter (μm) | Wavelengths (nm) |
|---|---|
| 8 to 10 | 1310, 1550 |
Single mode fiber is used for:
Telecommunications and networking. It sends voice, video, and data reliably.
Data centers. It connects servers and storage for cloud computing.
CATV systems. It gives clear TV signals with more bandwidth.
Industrial sector. It helps machines talk to each other in factories.
Military and defense. It keeps communication safe from outside signals.
Single mode fiber gives high bandwidth and low signal loss. You can send signals for miles without repeaters. This makes it good for backbone networks and fiber optic communication.
Multimode fiber optic cable has a bigger core. The core is usually 50 or 62.5 micrometers wide. This bigger core lets light travel in many paths. The light bounces off the cladding. You get more modal dispersion. The signals can mix and spread out. This limits how far you can send data before it gets weak.
Note: Multimode fiber is best for short distances and costs less than single mode.
Multimode fiber uses LEDs for light. The light travels in many paths. You need to repeat the signal for longer distances. You see multimode fiber in local networks, data centers, and schools.
Here is a quick look at how it works:
| Core Diameter (μm) | Wavelengths (nm) |
|---|---|
| 50 or 62.5 | 850, 1300 |
Multimode fiber is used for:
Corporate local area networks (LANs). It connects computers for fast data.
Manufacturing. It links machines and control systems.
Data centers. It helps servers talk to each other quickly.
Educational institutions. It gives students and staff good connections.
Multimode fiber costs less and is easy to install. It works well for short distances, like inside buildings or on a campus. These cables handle fast data for many users at once.
Here is a table that shows the main differences:
| Feature | Single-Mode Fiber | Multimode Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Core Diameter | 9 μm | 62.5 μm (OM1) or 50 μm (OM2/OM3/OM4/OM5) |
| Light Source | Laser or laser diode | LEDs |
| Signal Transmission | Nearly straight path | Multiple paths with reflection |
| Signal Loss | Lower over long distances | Higher, can bend more without breakage |
| Modal Dispersion | Minimal | Significant, needs repeaters |
| Typical Use | Long-distance networks | Medium-sized enterprises, LANs |
Callout: If you need to send data far and fast, use single mode fiber. For short distances and lower cost, multimode fiber is a good choice.
Now you know how each type works and what makes them different. Single mode fiber gives more bandwidth and longer distances. Multimode fiber is easier to install and costs less for short runs.
Single mode and multimode fiber optic cables work differently. Single mode fiber can send a lot of data very fast. It can handle hundreds of GHz. This means you can move lots of information quickly. The cable has a thin core. Light travels in one path inside it. This helps keep the signal strong. There is almost no mixing of signals. Your data stays clear, even when sent far away.
Multimode fiber has a bigger core. Many light pulses move through it at once. These signals can mix and spread out. This makes the bandwidth and distance lower. Multimode fiber works best at 850 nm and 1300 nm. OM5 multimode fiber can use more wavelengths. But it still cannot match single mode’s bandwidth.
Single mode fiber has no limit on modal bandwidth and can reach hundreds of GHz.
Multimode fiber works at 850 nm and 1300 nm, and OM5 can use more wavelengths.
Single mode fiber uses a thin core for fast, long-distance data.
Multimode fiber uses a bigger core for quick data over short distances.
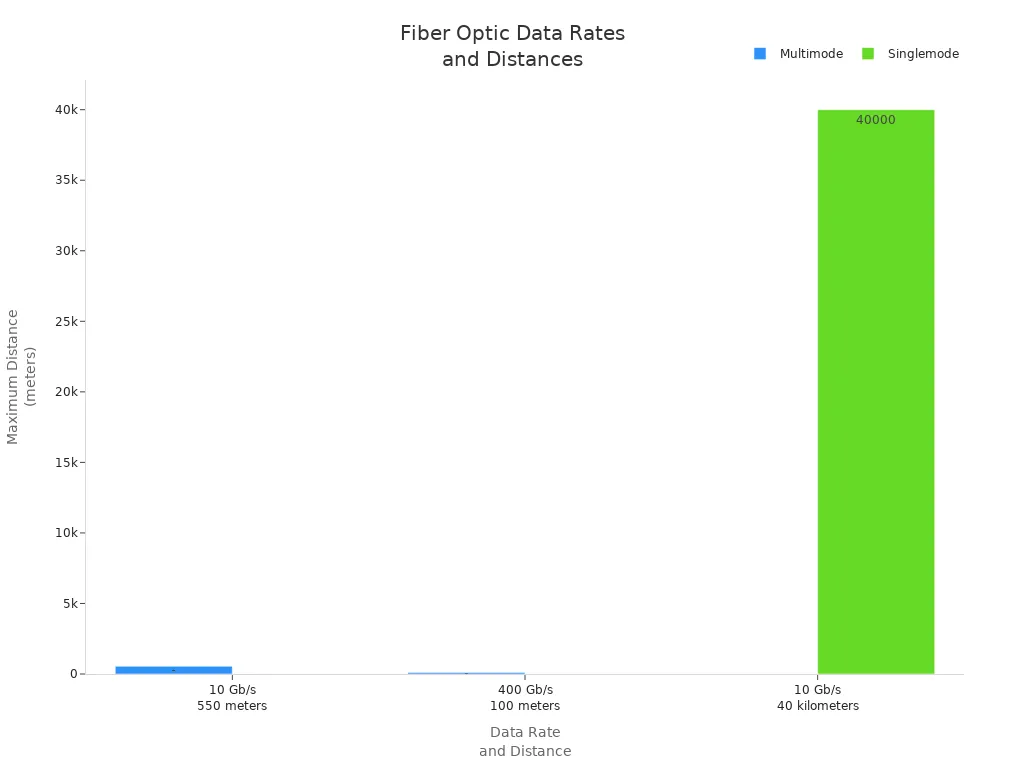
You should think about how far your data needs to go. Single mode fiber can send data up to 40-80 kilometers. That is about 25-50 miles. It can do this at 1 Gbps or 10 Gbps. Some special cables can go even farther, up to 160 kilometers. Some can reach over 200 kilometers. This makes single mode fiber best for long trips and global networks.
Multimode fiber is good for short distances. For example, OM2 multimode fiber can send data 550 meters at 1 Gbps. It can send 82 meters at 10 Gbps. You often see multimode fiber inside buildings or on school campuses. If you need to connect things across a city, single mode fiber is better.
| Fiber Type | Maximum Distance |
|---|---|
| Multimode (OM2) | 550m at 1Gbps, 82m at 10Gbps (less than 2km) |
| Single-mode | Up to 160km (over 200km with special fibers) |
Tip: If you need to send data far, single mode fiber is best.
Cost is important when picking a fiber optic cable. Single mode fiber costs more to set up. The cable itself is cheaper per foot. But the equipment you need costs more. You also need skilled workers to install it. The core is very small, so it is harder to work with.
Multimode fiber costs more per foot. But the equipment is cheaper and easier to use. You can install it fast. You do not need much training. For short runs inside a building, multimode fiber saves money.
| Cable Type | Material Cost (per foot) | Installation Cost (per mile) |
|---|---|---|
| Single Mode Fiber | $0.09 - $1.49 | $5,000 - $20,000 (underground) |
| Multimode Fiber (OM3/OM4) | $1.50 - $6.00 | $40,000 - $60,000 (aerial) |
Single mode fiber costs more at first but is best for long distances and fast speeds.
Multimode fiber is cheaper for short runs and is easy to install.
Note: The total cost depends on how far your data goes and what equipment you use.
Single mode and multimode fiber optic cables are used in different places. Single mode fiber is used for global networks. It connects cities, countries, and even continents. You see it in long-distance communication, underwater cables, telecommunication backbones, data centers, and 5G networks. It keeps signals strong and clear over long distances.
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Long-Distance Communication | Good for sending data far because it keeps the signal strong. |
| Underwater Cables | Used in cables that cross oceans and help the world connect. |
| Telecommunication Backbones | Needed for big networks between countries, with low delay and strong signals. |
| Data Centers | Used for fast, long-distance data with little signal loss. |
| 5G Infrastructure | Helps support fast internet and lots of data traffic. |
Multimode fiber is best for short distances. You see it in local area networks, data centers, schools, and offices. It is easy to put in and moves data fast over short spaces.
| Use Case | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Local Area Networks (LANs) | Good for sending data inside buildings or on campuses. | Cheaper, easy to install, fast data |
| Data Centers | Good for fast data over less than 300 meters. | Bigger core, cheaper parts |
Callout: Pick single mode fiber for long distances and lots of data. Choose multimode fiber for short, fast connections inside buildings.
Here is a table to help you pick the right fiber optic cable:
| Feature | Single Mode Fiber | Multimode Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Core Size | 8-10 μm | 50 or 62.5 μm |
| Light Transmission | Single path | Multiple paths |
| Bandwidth | Hundreds of GHz | Lower, but high for short runs |
| Maximum Distance | Up to 160 km (200+ km with special fibers) | Up to 2 km (usually less) |
| Data Rate | 10 Gb/s up to 40 km, 1 Gb/s for longer distances | 10 Gb/s up to 550 m, 400 Gb/s up to 100 m |
| Material Cost (per foot) | $0.09 - $1.49 | $1.50 - $6.00 |
| Installation Cost | $5,000 - $20,000 per mile (underground) | $40,000 - $60,000 per mile (aerial) |
| Equipment Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Installation | Needs skilled workers | Easier, less training needed |
| Typical Applications | Long-haul, backbone, data centers, 5G | LANs, data centers, campuses |
Note: Both types of fiber optic cables use light to send data. But they are used for different jobs. Think about how much data, how far, and how much money you have before you choose.
When you pick a fiber optic cable, you must think about a few things. These things help your network work well and last longer. Here are the main things to look at:
Distance: You should know how far your signals will go. Single mode cables have a core that is about 9µm wide. They keep data strong and clear over long trips. Multimode cables have bigger cores, like 50µm or 62.5µm. They can carry more data at once but lose power if the run is too long.
Bandwidth Needs: Think about how much data your network will send. Single mode cables can handle more data over long distances. Multimode cables are good for smaller jobs, like in homes or small offices.
Cable Construction: Check where you will put the cable. Indoor cables may need a different cover than outdoor cables. Outdoor cables often have jackets that block water and sun to protect them from bad weather.
Cost: Single mode cables usually cost more than multimode cables. You also need to think about how much the equipment and setup will cost.
Environmental Conditions: Hot, cold, or wet places can change how cables work. Pick cables that can handle the weather in your area. Outdoor cables can work from -40°F to 158°F. Indoor cables should stay dry and under 60% humidity to stop mold and damage.
Application Type: Decide if you need the cable for home, business, or big data networks. Each job has a best cable type.
Tip: Always pick the cable that fits your network’s needs. This helps you avoid trouble and saves money later.
You now know the main ways single mode and multimode fiber optic cables are different. Single mode has a small core. It uses laser light. This lets it send data far and fast. Multimode has a bigger core. It uses LED light. It works well for short distances and costs less. Think about how far your network needs to reach. Also, think about how fast you need it to be and how much you can spend. If you want your network to grow in the future, like for 5G or IoT, single mode is a smart pick. Always use good materials. Be gentle with the cables so you do not make mistakes.
| Feature | Multimode | Single-mode |
|---|---|---|
| Core Size | 50 to 62.5 microns | 8 to 10 microns |
| Light Source | LED | Laser |
| Distance | 300m – 550m | Up to 40 km |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Bandwidth | Lower | Higher |
Single mode fiber optic cable has a very thin core. It sends data far and fast. Multimode fiber optic cable has a thicker core. It works best for short distances and costs less. You pick one based on how far and fast your network needs to be.
You cannot connect single mode and multimode fiber optic cables right to each other. They have different light sources and core sizes. If you want to join them, you need special converters or adapters.
Think about how far and how fast your data must go. Use single mode fiber optic cable for long runs and lots of data. Choose multimode fiber optic cable for short, cheaper connections inside buildings.
Yes, fiber optic cables do not carry electricity. You will not get shocked. Always wear safety glasses and follow rules to keep your eyes safe from laser light.
You see fiber optic cable in internet networks, data centers, hospitals, schools, and phone systems. It moves lots of data quickly and does not fail often.